By Dr Tony Setiobudi BMedSci, MBBS, MRCS, MMed (Ortho), FRCS (Ortho)
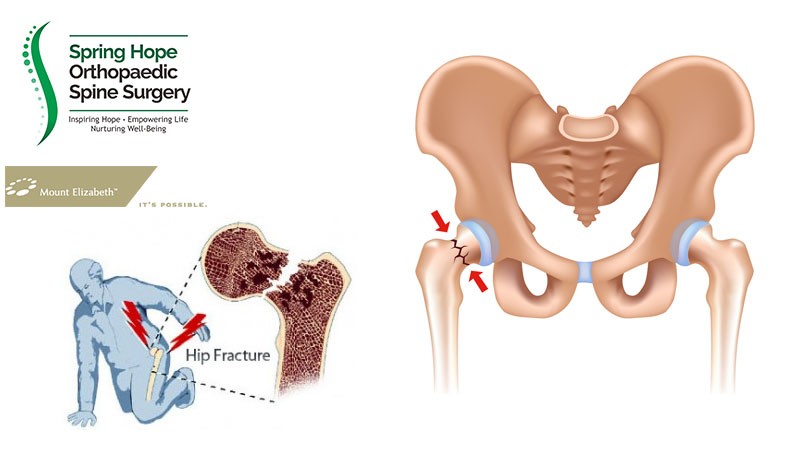
Hip fracture often occurs in elderly with osteoporosis after a trivial injury. It is important to know the cause of the fall which sometimes can be more life-threatening than the hip fracture itself.
What do I need to do if an elderly member of my family had a fall?
Firstly, you need to ensure that the patient is free from danger from the surrounding. Then you need to ensure that the patient is conscious and obey command. Please ask what the patient is feeling right now. Feeling headache or blurred vision with slurred speech may be a sign of stroke. Feeling chest pain and shortness of breath may be a sign of heart attack. If the patient is complaining of hip pain and is unable to walk, he or she may have hip fracture. You need to bring the patient to the hospital to get it checked and treated.
What do I do if the patient complains of hip pain and is unable to walk?
You can carry the patient to the bed or comfortable chair while supporting the injured leg. You need to check if the patient has other injuries. As there is a possibility of hip fracture, you need to bring him or her to the hospital. Let the doctor take over from here.
How is hip fracture detected?
There are several ways to detect hip fracture. Firstly, by doing thorough physical examination. The affected leg is shortened and rotated abnormally. The affected hip joint is very painful on movement. The patient like to keep the affected leg very still. Secondly, Xrays can confirm the diagnosis of hip fracture. From Xrays, the doctor can determine the type and the severity of the hip fracture.
What are the types of hip fractures?
The fracture in the hip can occur in the neck or below the neck of the femur. Fracture in the neck of the femur is called neck of femur fracture. Fracture below the neck of the femur is called intertrochanteric fracture. It is very important to differentiate the two as it influences the treatment.
How is hip fracture treated?
The first priority is to make sure that the patient is safe from danger. Sometimes they may have serious medical conditions that caused the fall e.g. stroke, heart attack, dehydration and so on. This must be treated first. Once the patient is stable, doctor can concentrate on the hip fracture itself. Generally, hip fracture is treated with surgery unless the patient is too ill to undergo surgery. Without surgery the chance of walking again is very slim. Therefore, whenever the patient is fit, surgery is the best option of treatment for hip fracture.
When should the surgery be performed?
Surgery should be performed as soon as possible for the following reasons. The muscle mass decreases with the duration of the immobility. Sometimes, after prolonged immobility it is difficult for the patient to walk again despite successful operation because the leg muscles are too weak. Secondly, prolonged immobilisation increases the risk of having blood clots in the leg. This condition is called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). By itself, DVT is not dangerous. It causes the affected leg to swell. However, when the blood clot migrates to the lung and block the main blood vessel, it can be fatal.
When can the patient start to walk after surgery?
Hip replacement surgery allows the patient to walk faster because it does not need to wait for the fracture to heal. The patient can start to walk with physiotherapist as early as the next day following the surgery. Sometimes, the patients are not allowed to walk immediately when the fracture is not stable and needs time to heal. In this case, the patient can move around with wheel chair. The patients need to exercise the muscles even though walking is not allowed. This is to preserve the muscle mass so that when the fracture has healed, the patient can walk immediately.

Dr Tony Setiobudi is an Orthopaedic & Spine Surgeon at Mount Elizabeth Hospital (Orchard), Singapore. He treats bone, joint, muscle and ligament problems in adults and children. He has a special interest in nerve compression and spine problems such as back & neck pain, scoliosis, kyphosis, spine tumor & infection, spinal cord injury, osteoporosis fracture, spinal stenosis and slipped disc.

